Inflammation plays a key role in many chronic diseases, from heart conditions to arthritis. The good news is that certain foods contain natural compounds that help reduce inflammation and promote overall wellness. In this post, we’ll explore 13 nutrient-rich foods that not only fight inflammation but also support healthy aging, immunity, and disease prevention. Adding these to your diet can be a simple yet impactful step toward better health.
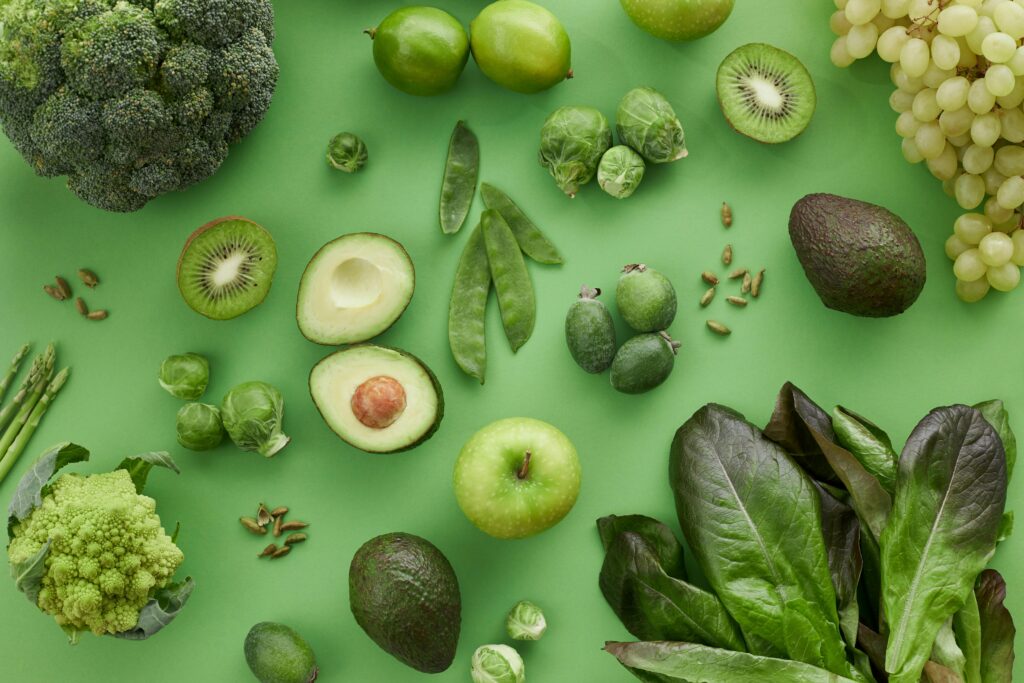

Many everyday foods contain compounds that help combat inflammation, potentially reducing the risk of chronic illnesses. Some of the most effective anti-inflammatory foods include fruits, vegetables, fish, and spices. Below is an overview of key foods and how they benefit the body:
- Berries
Berries such as strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries are rich in antioxidants called anthocyanins, which may reduce inflammation and lower the risk of diseases like cancer and heart conditions. Some research even shows berries support immune function by enhancing natural killer (NK) cells. - Fatty Fish
Fish like salmon, sardines, and mackerel contain omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA), known to lower markers like C-reactive protein (CRP), associated with inflammation. These fatty acids also help manage conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome by turning into compounds that actively reduce inflammation. - Broccoli
Broccoli, a cruciferous vegetable, is high in antioxidants like sulforaphane, which lowers inflammation by targeting harmful cytokines. Studies suggest that regular consumption of broccoli can help reduce risks associated with cancer and heart disease. - Avocados
Packed with healthy fats, fiber, and potassium, avocados contain carotenoids and tocopherols, both linked to reduced cancer and heart disease risks. Additionally, research shows avocados can lower inflammatory markers like interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) in adults with excess weight. - Green Tea
Green tea contains a powerful antioxidant called epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), which inhibits the production of inflammatory molecules. This beverage has been associated with a lower risk of conditions such as heart disease, Alzheimer’s, and obesity. - Peppers
Bell and chili peppers are loaded with antioxidants like quercetin and sinapic acid. These compounds are known to combat inflammation and support healthy aging. Chili peppers, in particular, may help reduce the inflammation associated with chronic illnesses such as diabetes. - Mushrooms
Certain types of mushrooms, including shiitake and portobello, are rich in B vitamins, selenium, and antioxidants. These nutrients provide anti-inflammatory effects and promote immune health, although cooking methods may affect their benefits. - Grapes
Grapes contain anthocyanins and resveratrol, antioxidants that help reduce inflammation and lower the risk of heart disease, arthritis, and diabetes. Studies suggest that resveratrol supplements may decrease inflammatory gene markers in individuals with heart conditions. - Turmeric
Turmeric’s active ingredient, curcumin, has potent anti-inflammatory properties. Research shows it can alleviate symptoms of arthritis and metabolic syndrome. However, since curcumin is hard to absorb, taking it with black pepper (which contains piperine) enhances its effectiveness. - Extra Virgin Olive Oil
A staple of the Mediterranean diet, extra virgin olive oil contains oleocanthal, which acts similarly to anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen. It also helps lower the risk of heart disease and reduces inflammation more effectively than refined oils. - Dark Chocolate and Cocoa
Dark chocolate, rich in flavanols, promotes cardiovascular health by reducing inflammation. Some studies show that cocoa flavanols improve vascular function and lower blood pressure shortly after consumption. Opting for chocolate with at least 70% cocoa content maximizes these benefits. - Tomatoes
Tomatoes are a great source of lycopene, an antioxidant with strong anti-inflammatory properties, especially when cooked with olive oil for better absorption. Lycopene has been linked to lower risks of cancer and other chronic conditions. - Cherries
Both sweet and tart cherries offer anti-inflammatory benefits due to their antioxidants, such as anthocyanins and catechins. Tart cherry juice, in particular, has been shown to reduce CRP levels in some studies, though more research is needed to confirm these effects.
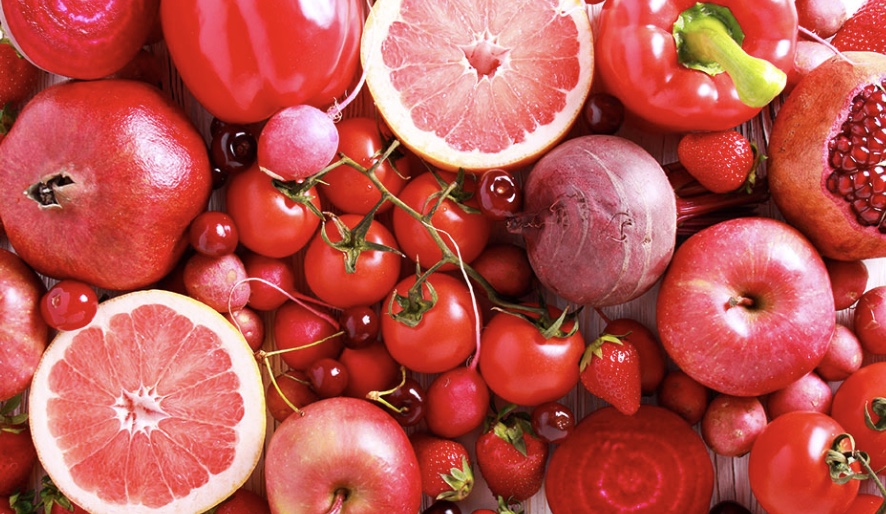

These foods not only taste great but also offer a natural way to manage inflammation, which is essential for long-term health and disease prevention. Incorporating a variety of these anti-inflammatory options into your diet can help improve well-being and reduce the risk of chronic illnesses.
EUROPEAN PERSPECTIVE:
Fighting Inflammation with Food according to The Guardian
Our modern environment, including changes in diet, air quality, and lifestyle, constantly activates the immune system, contributing to chronic, low-level inflammation linked to various diseases, explains Dr. Shilpa Ravella from Columbia University. Many inflammatory issues originate in the gut, where the microbiome—trillions of bacteria and organisms—interacts with immune cells to balance tolerance and defense. However, disruptions in this balance, influenced by genes and environmental factors, can lead to food allergies, inflammatory bowel disease, and other conditions.
Ultra-processed foods (UPFs), common in Western diets, may be a factor in gut inflammation. Although direct links between UPFs and inflammation are still being studied, additives and artificial sweeteners have been shown to alter gut bacteria in ways that promote inflammation. To counter chronic inflammation, experts recommend reducing refined foods and sugary beverages while focusing on whole, nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Spices like turmeric, ginger, and garlic offer additional anti-inflammatory benefits.
Omega-3-rich foods, such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, can further reduce inflammation, while avoiding excess alcohol supports gut health. Intermittent fasting may also help by promoting autophagy—the body’s natural process of clearing damaged cells. Additionally, regular exercise plays a role in reducing inflammation by preventing obesity and offering other health benefits.
sources: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/13-anti-inflammatory-foods#inflammatory-foods