WHAT IS YOGA:
Yoga is the belief that good health depends on a holistic approach to life – recognizing and working to enhance the mind-body-spirit connection, setting it apart from other forms of exercise. Yoga can be incorporated into your fitness program to increase your strength, enhance your flexibility and tone up your body as well as boost your capacity of concentration

HISTORY OF YOGA:
Traditionally, there are four “paths” of yoga with aim of reaching a higher plane of consciousness to attain a more balanced, calm state of being:
→ JNANA YOGA: involves the pursuit of knowledge
→ BHAKTI YOGA: path of devotion and compassion
→ KARMA YOGA: involves mindfulness and selfless action
→ RAJA YOGA: (later adaptation hatha yoga) is the most practiced in the West. Codified by Indian sage Patanjami between 200 BCE and 200 CE into a system called “ashtanga” yoga meaning “eight limbs”.
Yoga is introduced in the West in the late 19th century but became popular in the 1960s due to masters like Swami Vishnudevananda who proposed five principles of yoga: proper exercise, breathing, diet, relaxation and positive thinking and meditation
THE “EIGHT LIMBS” OF YOGA:
- YAMA: positive, external actions, such as non-violence, o stealing and truthfulness
- NIYAMA: positive, self-disciplined, internal “actions” such as cleanliness and self-study
- ASANAS: development of discipline through physical postures in preparation for meditation
- PRANAYAMA: breath control exercise to gain mastery over our internal energy, known as prana
- PRATYAHARA: sensory transcendence
- DHARANA: concentration
- DHYANA: meditation
- SAMADHI: spiritual enlightenment
CURRENT “TYPES” OF YOGA:
- HATHA: involves holding postures for quite a long time to achieve maximal stretching and relaxation (hatha yoga: “ha” means sun and “tha” moon so “hatha” is about uniting opposites for balance → ideal for “Take-it-easy” personalities
- LYENGAR: focuses on accurate body alignment and may use props such as blocks or straps to help you into the positions → ideal for “Get-up-and-go “ personalities
- ASHTANGA VINYASA: involves moving into each moving into each posture in rhythm with the breath → ideal for “Let’s-do-it” personalities
- BIKRAM: involves doing a series of 26 postures in rooms heated to about 35-40°C (95-105°F) to promote flexibility → ideal for “Let’s-do-it” personalities
- KUNDALINI: focuses on doing exercises to awaken the subtle energy within the body, known as “kundalini” which travels up through energy centers called chakras → ideal for “Get-up-and-go” personalities
- SIVANANDA: focuses on 5 principles of yoga and particularly on getting the most from twelve key postures by holding them for quite a long time to relax into them → ideal for “Take-it-easy” personalities
- JIVAMUKTI: means “liberation while living” combining intense exercise with music, meditation and chanting → ideal for “get-up-and-go” personalities
5 PRINCIPLES OF YOGA:
- PROPER EXERCISE:
→ build flexibility and keeping spinal are strong
→ keep nervous system healthy, the mind focused and soul nourished
- PROPER BREATHING:
→ deep & rhythmical breathing provides energy that the body needs but also clears harmful toxins
→ purifies body and mind
- PROPER DIET:
→ diet of fresh, healthy, easy-to-digest food to supply the body with vital energy it needs to function optimally
- PROPER RELAXATION:
→ regular and complete relaxation (physical and mental) is an essential way to restore energetic balance
- POSITIVE THINKING AND MEDITATION:
→ a balanced, strong and relaxed body increases clarity and peace of mind
→ meditation leads to awareness of what is really of value to you
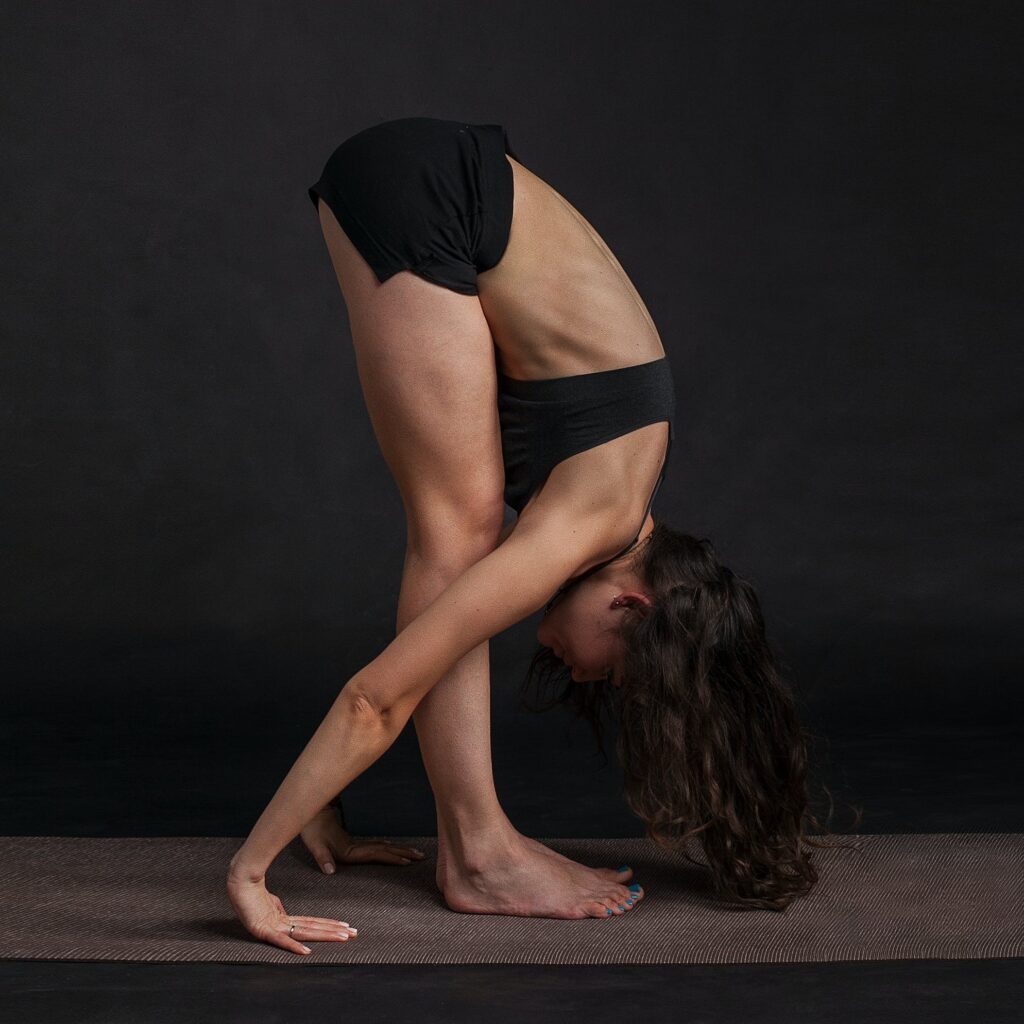

BENEFITS OF YOGA:
→ increase your overall strength, flexibility and it also nourishes, rebalances and relaxes you to re-energize you
→ allows areas of tightness and compression to unfurl causing a sense of increased lightness as well as improved posture
→ tone your body and appear more leaner
TYPES OF MOVEMENT:
- FORWARD BENDS
→ to massage internal organs (digestive ones) and length your spine
→ boost your concentration and calm your mind
- BACK BENDS
→ strengthen your spine and increases its mobility
- LATERAL BENDS
→ increases the sideways mobility of your spine
- TWISTS
→ releases tensions that’s in your back, massages abdomen and energizes your digestive system
- BALANCES
→ helps to develop a strong core and teaches you to focus your mind
- INVERSIONS
→ increases upper body strength and brings more blood to your heart which improves your circulation and your ability to concentrate
EXTRA INFORMATION:
- Yoga can be done at any time but traditionally vigorous practice would be done in the morning to fire up your body and gentle practice in the evening to encourage balance
- You should always wait 2-3 hours after eating before practicing
- It is recommended to hold a pose for little longer as long as it’s not causing you discomfort
- You can use props such as a block to help with alignment, posture and comfort or a belt or even a bolster which is ideal under your spine or knees to deepen relaxation
Examples of Yoga Mat
EUROPEAN PERSPECTIVE
Yoga Tips
8 keys to your personal yoga practice:
- Don’t set the bar too high: start slowly and simply
- Don’t get hurt
- Choose the right time
- Choose the right place
- Warm up sufficiently
- An adapted practice
- Savasana: the final relaxation
- Take classes regularly
source: The Fitness Book – DK & https://www.casayoga-paris.fr/pratique-personnelle-yoga.html